Magnesium is essential for more than 300 metabolic reactions in cells in concert with hundreds of enzyme systems. The chemical symbol for magnesium is Mg. Magnesium assists with the synthesis of nucleic acids, fats, and protein. Magnesium offsets calcium for properly controlled blood clotting. Magnesium holds calcium in teeth to make teeth more resistant to cavities. Although there is less than one ounce (about 19 grams) of magnesium in an adult body, it is a vital nutrient.
Most of the magnesium in the body is found in the skeleton, as seen in Figure 10-5. About one-quarter of the magnesium is found in muscles. Only one percent of the magnesium in the body is found outside of cells. Magnesium in blood cells has three forms: bound to proteins, in stable compounds, and as ionized magnesium (Mg++).
Aerobic energy production in the cell requires magnesium. The enzyme that controls the first four steps of the oxygen energy cycle requires magnesium for its activity. Deficiency of magnesium can slow down this energy-producing cycle
Figure 10-5 Magnesium is normally found inside cells.
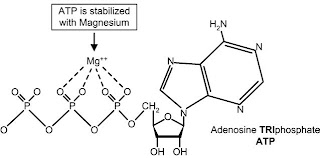
Figure 10-6 ATP is stabilized with magnesium.
Most energy production and energy transfer in cells use ATP, which exists as a complex with magnesium. When ATP is synthesized, magnesium is used to stabilize the phosphates, as seen in Figure 10-6.
More about Magnesium:
Most of the magnesium in the body is found in the skeleton, as seen in Figure 10-5. About one-quarter of the magnesium is found in muscles. Only one percent of the magnesium in the body is found outside of cells. Magnesium in blood cells has three forms: bound to proteins, in stable compounds, and as ionized magnesium (Mg++).
Aerobic energy production in the cell requires magnesium. The enzyme that controls the first four steps of the oxygen energy cycle requires magnesium for its activity. Deficiency of magnesium can slow down this energy-producing cycle
Figure 10-5 Magnesium is normally found inside cells.
Figure 10-6 ATP is stabilized with magnesium.
Most energy production and energy transfer in cells use ATP, which exists as a complex with magnesium. When ATP is synthesized, magnesium is used to stabilize the phosphates, as seen in Figure 10-6.
More about Magnesium:

0 comments